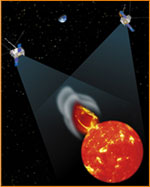
Mission Overview
STEREO - the third mission in NASA's Solar Terrestrial Probes program - launched on Oct. 25, 2006, aboard a single Boeing Delta II 7925 launch vehicle. This 2-year mission is employing two nearly identical space-based observatories, providing the first-ever, 3-D stereoscopic images of the sun. These images are helping scientists study the nature of coronal mass ejections or CMEs - powerful eruptions that can blow up to 10 billion tons of the sun's atmosphere into interplanetary space.
Traveling away from the sun at speeds of approximately one million mph, CMEs can create major disturbances in the interplanetary medium and trigger severe magnetic storms when they collide with Earth. Large geomagnetic storms can cause electrical power outages and damage communications satellites.
Despite the importance of CMEs, scientists don't fully understand their origin or evolution, nor their structure or extent in interplanetary space. STEREO's unique 3-D images of the structure of CMEs are enabling scientists to determine their fundamental nature and origin.
